Poor Listening Skills: Bad Habits That Hurt Communication
Poor listening skills are among the most common and damaging communication problems adults face. Many people believe they are good listeners, yet spend conversations mentally rehearsing responses, interrupting, or multitasking.
These habits reduce understanding, weaken relationships, and lead to frequent miscommunication. This guide breaks down the most common listening mistakes and explains how to listen with greater clarity, intention, and impact.
Key Takeaways
Poor listening skills often develop at a young age and continue into adulthood, shaping how a person listens, responds, and connects with others.
Listening skills improve with self-awareness and practice, even if poor listening feels automatic right now.
Active listening skills support better communication, stronger relationships, and clearer understanding of meaning.
Poor Listening Skills in Real Conversations
How Poor Listening Skills Hurt Communication
Active Listening Skills vs Hearing
Common Habits That Block Understanding and Connection
How to Improve Listening Skills in Daily Life
When Poor Listening Skills Point to Other Factors
Poor Listening Skills in Real Conversations
Poor listening skills describe patterns where a listener does not give full attention to the speaker. These patterns include interrupting, missing main points, or focusing on one's own thoughts instead of the message. Poor listening changes how words, meaning, and intent are received.
Listening skills involve hearing sound, processing language, and making sense of ideas. The brain must integrate words, tone, facial expressions, and body language simultaneously. When focus drops, understanding weakens.
Signs of Poor Listening in Daily Life
Poor listeners often rush ahead and respond before the speaker finishes talking. They may miss the point, forget details, or ask questions that were already answered. These behaviors signal low attention and weak listening skills.
Another sign is being easily distracted during conversation. Background noise, phones, or thinking about advice reduces focus. The speaker may feel ignored or misunderstood.
How Poor Listening Skills Develop Over Time
Poor listening often begins at a very young age when attention and language skills are still forming. A child may struggle to stay present during longer conversations. These patterns can follow a person into adult life.
Other factors include stress, hearing challenges, and fast-paced environments. These conditions affect how the brain processes sound and meaning. Over time, poor listening becomes a habit.
How Poor Listening Skills Hurt Communication
Poor listening skills weaken communication by disrupting the connection between the speaker and the listener. When a listener misses words or meaning, the message becomes unclear or wrong. This causes confusion and emotional distance.
Communication depends on shared understanding. Listening shows interest, respect, and care. Without good listening, conversations feel shallow or tense.
Poor Listening Skills in Relationships
In personal relationships, poor listening leads to frustration and hurt feelings. The person speaking may feel unimportant or unheard. Trust fades when listening problems repeat.
Listening helps people feel present and valued. Good listening supports empathy and emotional safety. These qualities strengthen relationships.
Poor Listening Skills at Work and School
At work, poor listening affects teamwork and feedback. Missed instructions and weak responses slow progress. Difficult conversations become harder to manage.
Listening skills support clear explanation and shared goals. When listeners understand the main points, communication improves. This leads to better outcomes.
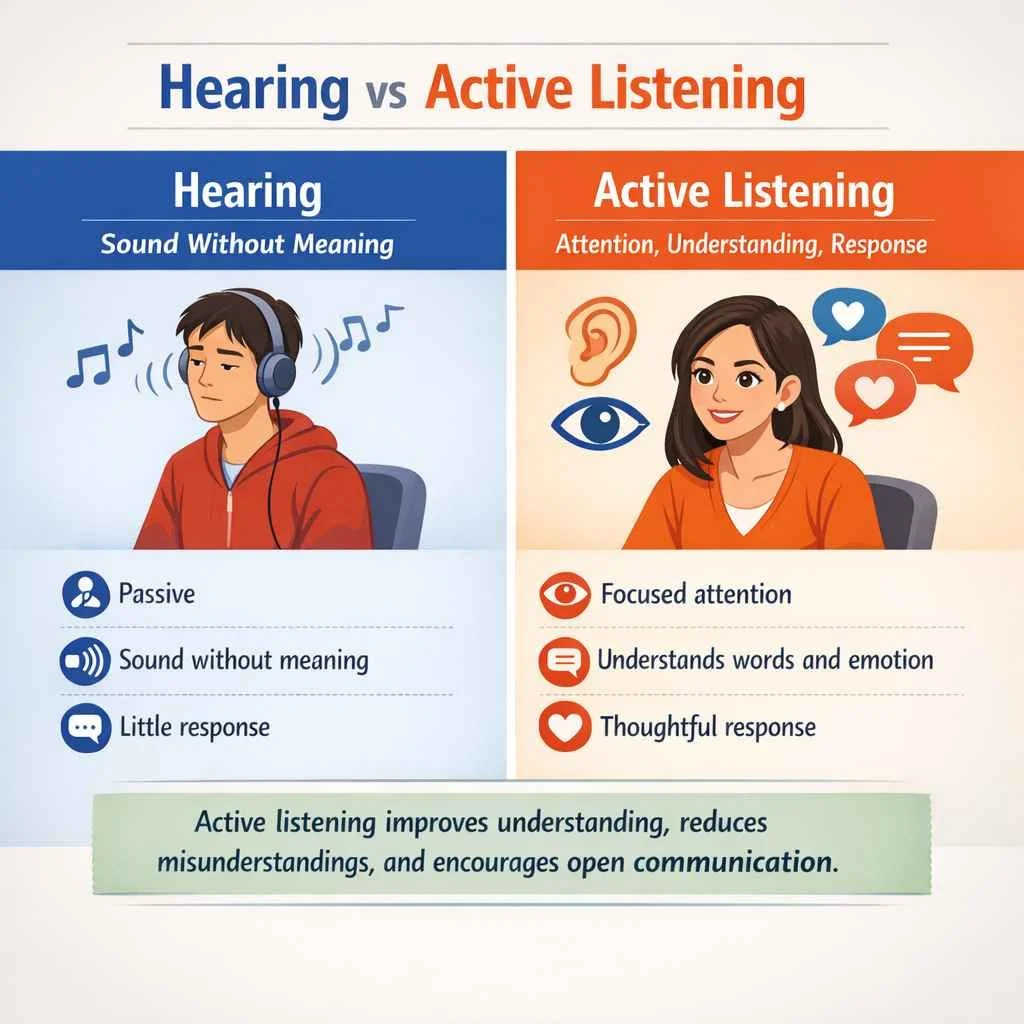
Active Listening Skills vs Hearing
Hearing refers to detecting sound. Listening requires focus, meaning, and response. Many people hear words but do not fully listen.
Active listening involves paying attention to words, tone, body language, and facial expressions. The listener stays present in the moment. This improves understanding and connection.
Active Listening Skills That Improve Listening
Active listening skills include eye contact, a still posture, and waiting to respond. These behaviors show interest and respect. They help the speaker feel heard.
Another skill is to reflect on what was said in your own words. This checks the meaning and reduces confusion. It also encourages deeper conversation.
Why Active Listening Supports Good Listening
Active listening helps the listener grasp deeper meaning and emotion. Responses become clearer and more accurate. Misunderstandings decrease.
Good listening encourages the speaker to share more ideas. This creates open communication. Both people benefit.
Hearing vs Listening
Check out our blog about hearing vs listening to understand their differences.
Common Habits That Block Understanding and Connection
Many adults engage in poor listening habits without realizing it. These patterns interfere with understanding, reduce connection, and lead to miscommunication. Recognizing these habits is the first step toward more effective listening.
Interrupting and Rushing Ahead
Interrupting disrupts the speaker’s train of thought and signals that the listener is no longer fully engaged. Rushing ahead and assuming the message is complete before it is often leads to incorrect conclusions and missed details.
Pausing before responding allows the brain time to process information. This improves comprehension and leads to more thoughtful, accurate responses.
Focusing on Your Own Thoughts
When attention shifts inward to personal thoughts or planned responses, the brain stops fully processing the speaker’s words. As a result, important meaning and nuance are lost.
Actively redirecting attention back to the speaker strengthens listening focus. With practice, this awareness improves overall communication effectiveness.
Distraction From Background Noise and Environment
Background noise and visual distractions compete for the brain’s attention, making it harder to process spoken language. Even minor environmental interruptions can significantly reduce focus.
Choosing quieter environments and minimizing distractions supports better listening. These small adjustments improve clarity and make conversations more productive.
How to Improve Listening Skills in Daily Life
You can improve listening skills through practice, awareness, and patience. Progress happens at your own pace. Small changes add up.
Stay Present and Give Full Attention
Giving full attention means facing the speaker and listening without multitasking. This signals respect and interest. It also helps the brain stay focused.
Noticing when attention drifts allows you to refocus. Each return builds better listening habits. Presence improves understanding.
Use Open-Ended Questions to Improve Listening
Open-ended questions help clarify ideas and feelings. They invite the speaker to explain more. This supports shared meaning.
Questions show interest and care. They help the listener understand the point. Conversation flows more easily.
Note Taking for Better Listening
Note-taking supports memory and focus during longer or difficult conversations. Writing key words helps organize ideas. This supports understanding.
Notes reduce mental overload. The listener can stay present. Attention improves.
How Poor Listeners Can Deliver Feedback
Deliver feedback only after fully listening. Responding too quickly increases the risk of a wrong response. Thoughtful feedback shows respect.
Repeating the message in your own words confirms understanding. This improves communication. The speaker feels heard.
When Poor Listening Skills Point to Other Factors
Poor listening can be related to stress, anxiety, or hearing changes. These factors affect attention and processing. Support can help identify them.
Speech-language pathologists assess listening, language, and communication patterns. Guidance supports clearer communication.
Self Awareness and Listening Skills
Self-awareness helps you notice your listening habits in real time. Awareness creates choice. Change begins there.
Personal experience often reveals patterns. Recognizing triggers helps reduce poor listening. Growth follows awareness.
Frequently Asked Questions About Poor Listening Skills
1. What causes poor listening skills in adults?
Poor listening skills in adults often result from distraction, stress, and habits formed at a young age. Many people never learned how to stay focused during a conversation. Background noise, fast thinking, and planning a response also interfere. These patterns continue without awareness.
2. Can poor listening skills harm relationships?
Poor listening skills harm relationships by reducing trust and emotional connection. People feel dismissed when they are not heard. Misunderstandings increase. Communication becomes strained.
3. How can I become a better listener?
Becoming a better listener starts with paying full attention to the speaker. Focus on words, tone, and body language. Ask open-ended questions to clarify meaning. Practice improves listening over time.
4. Are listening skills learned or natural?
Listening skills are learned behaviors that develop over time. Some begin at a young age, while others form later. Practice and guidance strengthen them. Improvement is possible at any stage.
How Connected Speech Pathology Can Help
Connected Speech Pathology provides online communication coaching for adults who want to strengthen their listening and communication skills. We work with clients who struggle to stay focused in conversations, miss key details, or find it difficult to respond clearly and effectively. Our licensed communication coaches offer practical, real-world strategies that translate directly into everyday interactions.
Our approach emphasizes active listening, sustained attention, and self-awareness. Sessions are flexible and designed to fit client schedules. The goal is simple: clearer understanding, more confident responses, and stronger communication overall.
Summary
Poor listening skills affect communication, relationships, and daily interactions. These habits often form early and continue without awareness. With practice and guidance, listening skills can improve. Better listening supports clearer understanding and a stronger connection.
About the Author
Allison Geller is a communication coach, speech-language pathologist, and founder of Connected Speech Pathology, an international online practice providing professional communication coaching and speech therapy for children, teens, and adults. With more than two decades of experience, she has worked in medical and educational settings, published research on aphasia, and leads a team of specialists helping clients improve skills in public speaking, vocal presence, accent clarity, articulation, language, fluency, and interpersonal communication.